Python Point Cloud Geometric Roughness
October 2022
In this project, I challenged myself to recreate the geometric roughness analysis from the CloudCompare software in Python. The original code was written in C++, and it measures roughness by creating a best fitting least square plane based on neighbouring points, where the neighbours are points that are within a certain radius of the point being analysed. From there the roughnesss is determined to be the distance the point being analysed is from the best fitting plane.
I recreated this method on python using the functions and libraries available on there. Some of the major libraries that was used to achieve this was Laspy, Numpy, and Scipy to name some.
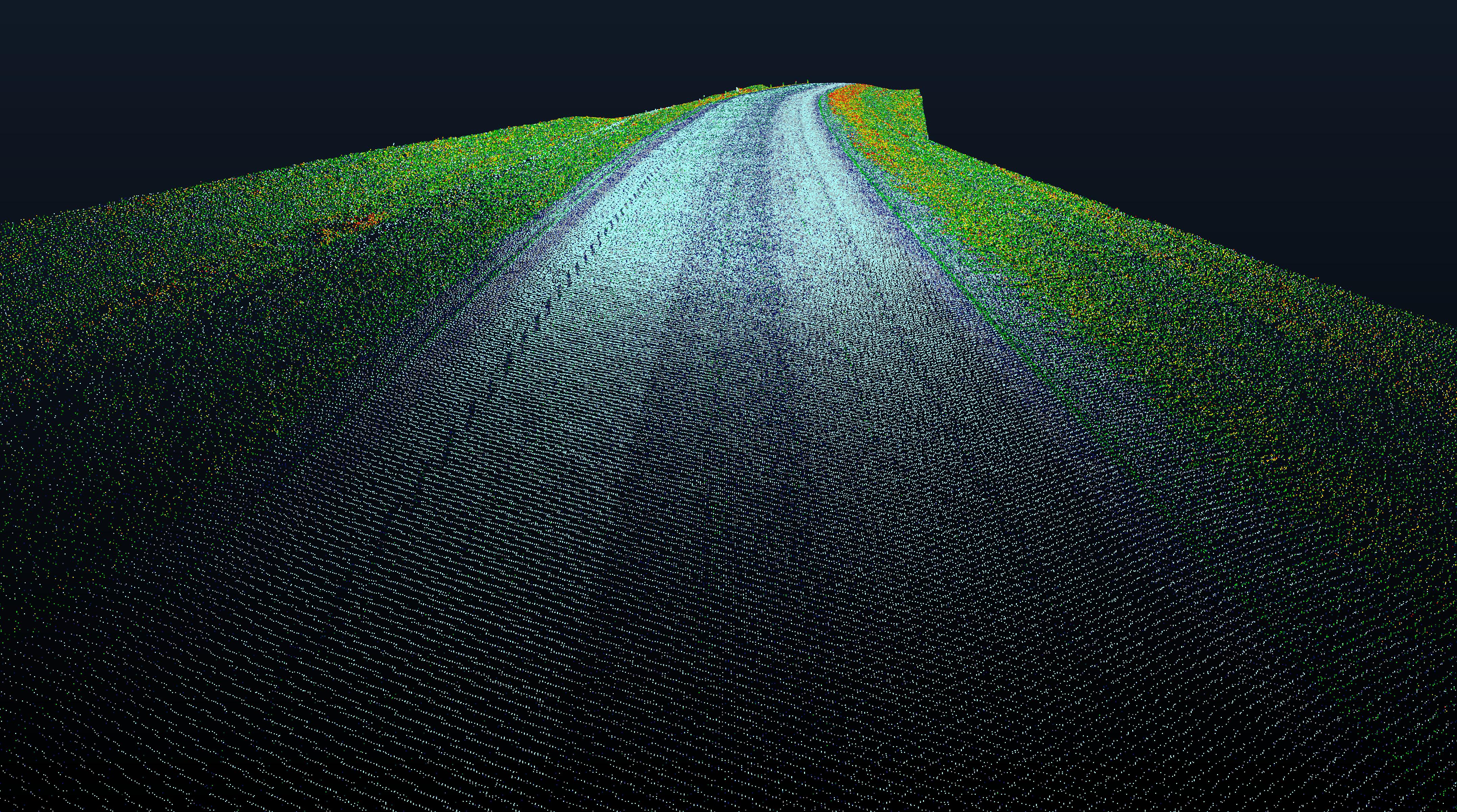
The resulting output from running Python point cloud roughness on a sample LiDAR input was identical to those from the CloudCompare geometric roughness calculations. I was very proud of the result that was achieved by this program.